What is Zero Trust architecture?
Zero Trust architecture is a security framework that operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” Unlike traditional security models that rely on perimeter defenses, Zero Trust assumes that threats can originate both outside and inside the network. Therefore, it continuously validates the trustworthiness of every entity attempting to access resources, regardless of their location.
Key components of Zero Trust include strict identity verification, least-privilege access, and continuous monitoring. Every user and device must be authenticated and authorized before gaining access to any resource. Access permissions are granted based on the minimum necessary to perform a task, reducing the risk of unauthorized actions. This principle of least privilege limits the potential impact of breaches.
Additionally, Zero Trust employs continuous monitoring and real-time assessments to detect and respond to anomalies. Network segmentation further isolates resources, ensuring that even if an attacker breaches one segment, they cannot easily access others. This granular control and scrutiny help prevent lateral movement within the network.
Zero Trust architecture enhances security by minimizing assumptions of inherent trust and focusing on rigorous access controls and real-time threat detection. It is particularly effective in today’s landscape of cloud computing and remote work, where traditional network boundaries are blurred.
What is the Zero Trust model?
The Zero Trust model is a cybersecurity approach that emphasizes verifying every access request as though it originates from an open network. It operates on the principle that no user or system, whether inside or outside the network perimeter, should be trusted by default. Each access request is evaluated based on stringent authentication and authorization policies, often incorporating multi-factor authentication (MFA) and device health checks.
The model also incorporates micro-segmentation, breaking down security perimeters into small, manageable zones to limit the spread of potential breaches. Dynamic, context-aware policies adjust access permissions based on factors such as user role, device security posture, and the sensitivity of the data being accessed.
By continuously validating all requests and enforcing fine-grained access controls, the Zero Trust model mitigates the risks associated with advanced threats and insider attacks. It provides a robust framework for securing modern, decentralized IT environments, including cloud services and remote workforces.
How Zero Trust works
Zero Trust works by implementing a rigorous set of security principles and practices designed to ensure that no entity, whether inside or outside the network, is trusted by default. Here’s how it operates:
- Verification and Authentication: Every access request is authenticated using robust methods like multi-factor authentication (MFA). This ensures that users and devices are who they claim to be.
- Least Privilege Access: Access rights are granted based on the principle of least privilege, meaning users and devices are given the minimum level of access required to perform their tasks. This minimizes the potential damage from compromised accounts or devices.
- Continuous Monitoring: Zero Trust involves continuous real-time monitoring of all network activity. Behavioral analytics and machine learning are often employed to detect anomalies and potential threats.
- Micro-Segmentation: The network is divided into small, isolated segments to limit lateral movement. If a breach occurs in one segment, it does not automatically grant access to other segments.
- Context-Aware Policies: Access decisions are based on a variety of contextual factors, such as user role, location, device health, and the sensitivity of the data being accessed. Policies dynamically adjust based on these factors.
- Automation and Orchestration: Automated responses to detected threats help to quickly mitigate risks. Orchestration tools ensure that security policies are consistently applied across the entire network.
By integrating these components, Zero Trust creates a robust, adaptive security posture that protects against both external and internal threats, ensuring comprehensive protection in complex, modern IT environments.
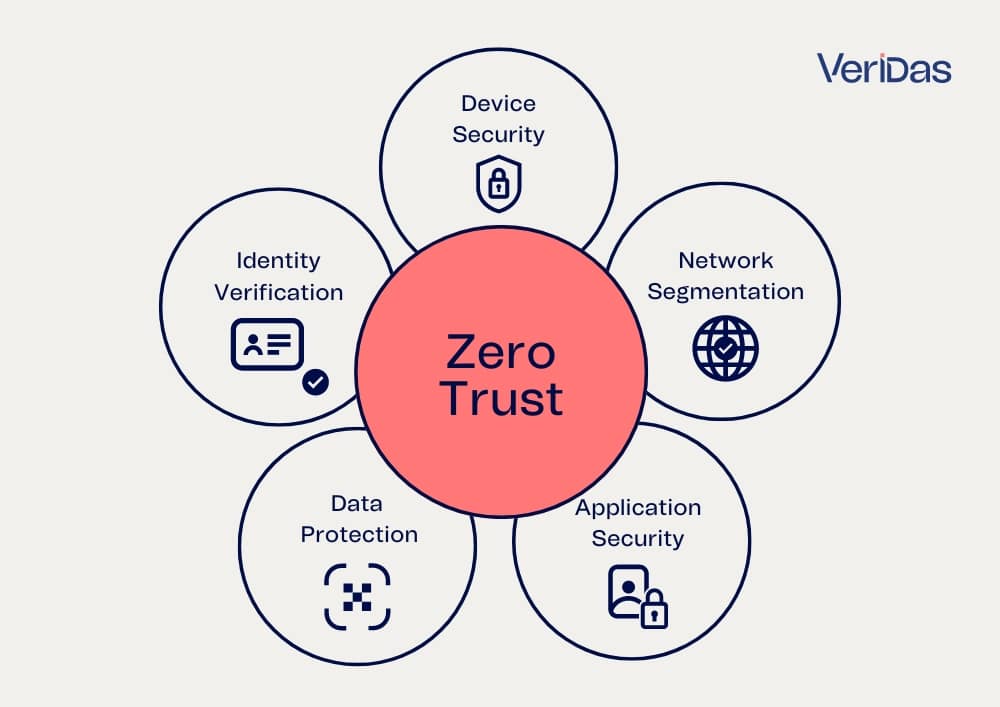
What are the 5 principles of Zero Trust?
The Zero Trust model is built on five foundational pillars that collectively enhance an organization’s security posture. These pillars are:
- Identity Verification: This pillar emphasizes the importance of verifying the identity of users, devices, and services before granting access to resources. It involves robust authentication methods, including multi-factor authentication (MFA), to ensure that only legitimate entities can access the network.
- Device Security: Ensuring that devices accessing the network are secure is crucial. This pillar includes checking the security posture of devices, such as their compliance with security policies and their health status. Devices that do not meet security standards are denied access or given restricted access.
- Network Segmentation: Also known as micro-segmentation, this pillar involves dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments. Each segment is protected individually, which limits the ability of attackers to move laterally within the network if they breach one segment.
- Application Security: This pillar ensures that applications are secure and only accessible by authenticated and authorized users. Application-level controls, such as application whitelisting and runtime protection, help safeguard applications from unauthorized access and vulnerabilities.
- Data Protection: Protecting sensitive data is a core component of Zero Trust. This pillar involves encrypting data both at rest and in transit, as well as implementing strict access controls. Data is classified based on its sensitivity, and access is granted on a need-to-know basis.
These pillars collectively ensure a robust, multi-layered defense strategy, minimizing the risk of breaches and enhancing overall security.
What is zero trust security?
Zero Trust security is a cybersecurity paradigm that assumes no user or device, whether inside or outside the network, is inherently trustworthy. It mandates continuous verification and strict access controls for every access request.
By employing multi-factor authentication, micro-segmentation, and real-time monitoring, it ensures that only authenticated and authorized entities can access resources.
The approach dynamically adjusts security policies based on contextual factors such as user roles and device health, effectively minimizing risks and preventing unauthorized access and lateral movement within the network. This model is especially pertinent for modern, cloud-based, and remote work environments.
What is an example of Zero Trust?
Zero Trust security, when applied to Veridas Voice Shield, ensures that every voice interaction is continuously authenticated to protect against deepfake and other audio-based frauds. This solution involves real-time verification of voice authenticity without relying on user registration or consent, thereby reducing friction.
Voice Shield leverages advanced AI algorithms to distinguish between genuine and fraudulent voices by analyzing specific voice properties. This approach aligns with Zero Trust principles by treating every voice interaction as potentially untrusted and requiring continuous verification to secure sensitive communications and prevent fraud.
Zero trust solutions
Zero Trust solutions applied to Veridas’ offerings focus on stringent identity verification and authentication measures across digital and physical domains. Veridas employs advanced biometrics, such as facial recognition and voice recognition, to authenticate users securely and seamlessly.
These solutions ensure that access to systems and data is continuously verified, aligning with Zero Trust principles by treating every access request as untrusted by default.
Veridas’ solutions includes identity verification for digital onboarding, secure access control, and real-time fraud detection, providing comprehensive protection against unauthorized access and identity fraud.
What is zero trust network access?
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is a security framework that ensures secure, authenticated access to applications and data. It operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify,” meaning every access request is rigorously authenticated, authorized, and encrypted. ZTNA continuously assesses the security posture of users and devices, granting the least privilege access necessary.
This minimizes potential attack surfaces by dynamically adapting security policies based on real-time context and user behavior, thereby enhancing protection against internal and external threats.
What is the main goal of Zero Trust?
The main goal of Zero Trust is to enhance security by eliminating implicit trust within an organization’s network. It continuously authenticates and verifies every user and device seeking access to resources, regardless of their location.
This approach ensures that only authorized entities with verified identities and appropriate security postures can access sensitive data and systems.
By applying strict access controls and real-time monitoring, Zero Trust minimizes the risk of breaches, limits potential attack surfaces, and prevents lateral movement within the network, thus providing robust protection against both internal and external threats.








