Securing our identity has become a top priority in an increasingly digitalized world. Traditional authentication methods, such as passwords, have proven vulnerable and ineffective. In this context, Renewable Biometric References (RBRs) emerge as an innovative and promising solution.
RBRs are abstract and mathematical representations of a person’s biometric traits. They do not store direct data from these traits, thus preventing the reconstruction of the original information.
Unlike traditional biometric templates, which store fixed representations of facial traits, RBRs are dynamic and adapt to the context in which they are used.
These references analyze between 500 and 600 distinctive features of a person and are defined in the ISO/IEC 24745:2022 standard.
To better understand this, let’s first explain what traditional biometric templates are and how they work.
What is a biometric template?
Traditional biometric templates are mathematical representations of a person’s facial traits. Unlike traditional images, a biometric template does not store a photo of the face but a set of numerical data describing the relationship between various key facial points, such as the distance between the eyes or the shape of the nose.
How Traditional Biometric Templates Work
- Image Capture: A facial image is captured using a camera.
- Trait Analysis: 60 to 80 key points on the face are identified.
- Template Generation: These key points are converted into numerical data that form the biometric template.
- Storage and Comparison: The template is stored and compared with new facial images for future authentication attempts.
Characteristics of biometric templates
- Uniqueness: Each person generates a unique biometric template based on their facial traits.
- Reversibility: The original face can be reconstructed from the template.
- Interoperability: Templates can be reused across multiple systems for different purposes.
- Irrevocability: Biometric templates cannot be modified or revoked once created.
- Vulnerability: Templates are susceptible to attacks and breaches, especially when stored in centralized databases.
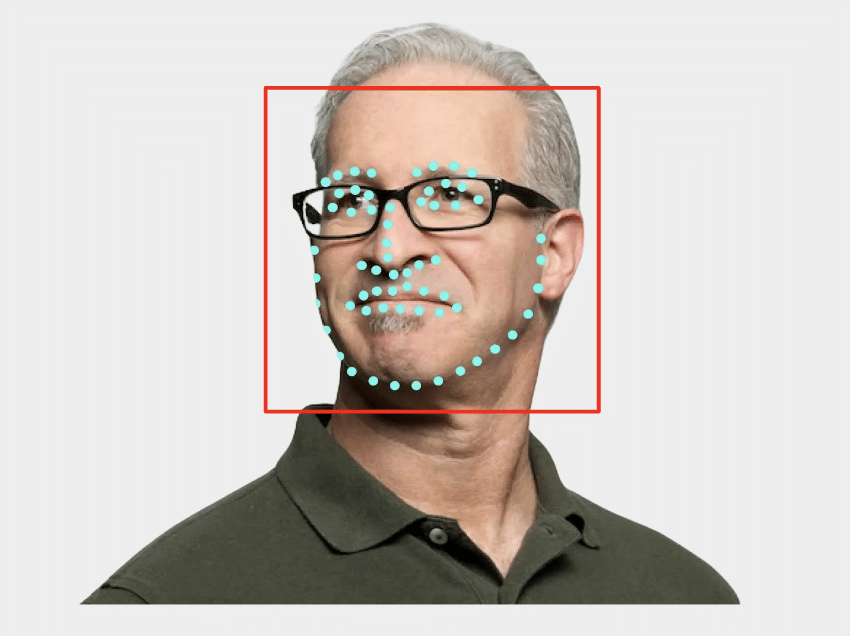
What are Renewable Biometric References (RBRs)?
RBRs represent a technological evolution that addresses the limitations and risks of traditional biometric templates. They are abstract, mathematical representations of a person’s biometric traits that do not store direct data from these traits. RBRs are defined in the ISO/IEC 24745:2022 standard.
How Renewable Biometric References Work
- Image Capture: A facial image is captured using a camera.
- Trait Analysis: The system analyzes between 500 and 600 distinctive facial features.
- RBR Generation: A mathematical positional representation of biometric traits is created, which does not store direct facial data.
- Encryption: The RBR is encrypted for protection.
- Authentication: A new RBR is generated from the current facial image and compared with the stored RBR.
Renewable Biometric References Features
- Multiplicity: Different systems generate distinct RBRs for the same face, adapting to specific contexts or applications.
- Irreversibility: It is impossible to reconstruct the original face from an RBR.
- Non-Interoperability: RBRs can only be interpreted by the system that created them.
- Revocability: RBRs can be easily revoked and replaced if suspected of being compromised.
- Security: They provide a high level of data protection and privacy, complying with regulations like GDPR.

Tradicional Biometric Templates vs. Modern Biometrics
| Feature | Tradicional Biometric Templates | Renewal Biometric References (RBRs) |
| Uniqueness/Multiplicity | One template per person. | Multiple RBRs per person adapted to cthe ontext. |
| Reversibility/Irreversibility | Face reconstruction possible. | Reconstruction is impossible. |
| Interoperabilidad/No interoperabilidad | Reusable across multiple systems. | Limited to the system that created them. |
| Irrevocabilidad/Revocabilidad | Not modifiable or revocable. | Easily revocable and replaceable. |
| Seguridad | Higher risk of breaches. | Higher security and privacy by design. |
Use Cases of RBRs
RBRs are used to authenticate a person’s identity securely and privately in both physical and digital environments. Their primary goal is to prevent identity theft and protect users’ personal data. Applications include:
- Facial access control: To enter buildings, devices, or applications.
- Biometric identity verification: In banking transactions, government services, or e-commerce.
- Airport Security: To streamline boarding processes and enhance safety.
- Digital Signatures: To validate documents and electronic transactions.
RBRs: Present and Future of Secure Identity
Renewable Biometric References represent a crucial step forward in protecting digital identity, offering a secure and private alternative to traditional biometric templates and password-based authentication methods. Their adoption is increasingly vital as digitalization and sophisticated cyberattacks demand robust, privacy-respecting authentication solutions.
- Challenges with Passwords:
Despite their widespread use, passwords are increasingly vulnerable and costly for both individuals and businesses. Phishing attacks, credential theft, and poor password management practices jeopardize user security and trust. - Limitations of Traditional Templates:
While an improvement over passwords, traditional biometric templates have significant privacy and security risks due to their uniqueness, reversibility, interoperability, and irrevocability. Once compromised, the person is permanently exposed. - Advantages of RBRs:
Designed to address these issues, RBRs combine advanced security features with privacy principles, ensuring:- Distinct RBRs for the same face across different systems.
- No possibility of reconstructing the original face.
- Non-interoperable references specific to their originating system.
- Easy revocation and replacement if compromised.
- Compliance and Data Protection:
RBRs adhere to privacy-by-design and privacy-by-default principles, making them ideal for markets seeking secure, privacy-focused solutions, as required by GDPR. This technology ensures users have control over their data and sovereignty over their information.
The adoption of RBRs is not just necessary but represents a decisive technological leap in safeguarding digital identity.
These references provide a robust alternative to passwords and traditional biometric templates by integrating advanced security with embedded privacy principles.
Implementing RBRs mitigates the risks of traditional authentication systems, fostering greater trust in digital interactions and technology use.